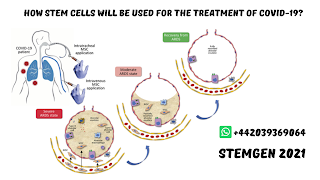
How Stem cells will be used for the Treatment of COVID-19?
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells are investigational items that have been read widely for wide
clinical applications in regenerative medicine1 and for their immunomodulatory
properties.2 It is theorized that mesenchymal immature microorganisms could
lessen the intense lung injury and restrain the cell-intervened provocative
reaction initiated by SARS-CoV-2.
Rationale for Use in
COVID-19
Mesenchymal
stem cells are multipotent grown-up undifferentiated cells that are available
in most human tissues, including the umbilical line. Mesenchymal stem cells can
self-reestablish by partitioning and can separate into various sorts of tissues
(counting osteoblasts, chondroblasts, adipocytes, hepatocytes, and others),
which has prompted a hearty clinical exploration plan in regenerative
medication. It is speculated that Mesenchymal stem cells could lessen the
intense lung injury and restrain the cell-interceded fiery reaction actuated by
SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, in light of the fact that they do not have the
angiotensin-changing over chemical 2 (ACE2) receptor that SARS-CoV-2 uses for
viral passage into cells, Mesenchymal stem cells are impervious to
contamination.
No
Mesenchymal stem cells items are supported by the Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) for the treatment of COVID-19. There are restricted information to date
to survey the job of mesenchymal undeveloped cells for the treatment of
COVID-19.
Information
supporting the utilization of Mesenchymal stem cells in patients, who have
viral contaminations, including SARS-CoV-2 disease, is restricted to case
reports and little, open-name contemplates.
Clinical Data for Other
Viral Infections
In an
open-name investigation of Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of H7N9 flu
in China, 17 patients got Mesenchymal stem cell treatment in addition to
standard of care, and 44 patients got standard of care as it were. Three
patients (17.6%) in the Mesenchymal stem cell arm kicked the bucket versus 24
patients (54.5%) in the norm of care arm. The 5-year follow-up was restricted
to five patients in the Mesenchymal stem cell arm. No security concerns were
recognized.
Risks
related with mesenchymal undeveloped cell bonding give off an impression of
being extraordinary. The potential dangers incorporate the potential for
mesenchymal stem cells to duplicate or change into improper cell types, item
tainting, development of cancers, contaminations, clots arrangement, and organization
site responses.

Comments
Post a Comment