Lung Regeneration
Introduction
Regenerative
medication can possibly give creative new treatments to individuals with lung
illnesses, including constant obstructive pneumonic infection (COPD),
aspiratory fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, pneumonic blood vessel hypertension and
bronchiolitis obliterans. Presently, end-stage lung illness is treated with an
array of drugs or at last, lung transplantation. Be that as it may, there is a
continuous lack of giver lung tissue agreeable to transplantation.
Examination
into lung conservation, lung recellularization and undifferentiated organism
science in the Center for Regenerative Medicine is prompting the advancement of
new regenerative treatments for individuals with a wide scope of lung
infections.
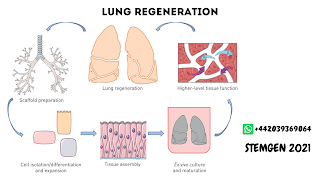
Recellularization
of decellularized lungs
Researchers
are concentrating on lung decellularization and recellularization methods to
advance toward an objective of on-request creation of patient-explicit,
relocate prepared lungs. Lung decellularization includes eliminating every one
of the cells from a giver lung, leaving behind the local design that can be
repopulated (recellularized) with initiated pluripotent stem (iPS) cells
obtained from the patient's own tissues. Mayo scientists are attempting to
create a working lung that is reasonable for transplantation by first
recellularizing an acellular porcine lung. Given promising outcomes in creature
models, Investigators are currently endeavoring to recellularize human lungs.
Continuous work includes separating iPS cells into lung-explicit cells for
recellularization.
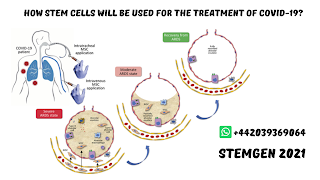
Stem cell
engineering
To
all the more likely see how to viably and reliably deliver patient-explicit iPS
cells for lung-related clinical application, Researchers are leading a clinical
preliminary in which iPS cells can be created from little skin biopsies taken
from patients with end-stage lung disease. Examiners trust that with additional
exploration, iPS cells could be separated into patient-explicit aspiratory
epithelial cells and conveyed back to patients by means of cell treatment.
These cells could likewise be utilized to repopulate acellular lung platforms
for implantation.
Tissue engineering
In spite of the fast advances in getting lung epithelial ancestries from
ESCs and iPSCs, the age of mind boggling 3D tissue structures, or even
utilitarian organs, from these cells stays a high obstacle. A quickly arising
space of examination meaning to address this test is the utilization of
tissue-designing ways to deal with create complicated, multicellular
constructions that may impersonate utilitarian lung tissues. Cylinders formed
like upper aviation routes, like windpipe and bronchi, have effectively been
designed in vitro, covered with different cell arrangements, for example, bone
marrow subordinates and precisely joined into patients who have areas of
tracheal or bronchial atresia. Up until now, there has been an inclination to
allude deep down marrow or other cell arrangements used to cover these aviation
route joins as undifferentiated organisms without obvious proof that they are
valid immature microorganisms.
Past the fruitful age of useful cylinders to direct wind stream, the
designing of utilitarian alveolar tissue for use in vivo stays a neglected
test. One invigorating methodology is the utilization in creature models of
'decellularization' by perfusion of cleansers through extracted entire lungs to
get ready 3D frameworks containing exclusively lung extracellular lattice.
Recellularization of this platform with epithelial cell lines (A549 or C10),
endothelial cells, mesenchymal immature microorganisms (MSCs), entire lung
cell–suspension processes or separated ESCs or iPSCs has been utilized in
evidence of-idea contemplates. The subsequent recellularized lungs can be
ventilated and perfused with blood and their fractional capacity, including
limit with respect to gas trade, has been exhibited through an assortment of
physiological estimations. A few examiners have even achieved orthotopic transplantation
of these bioartificial lung joins into pneumonectomized rodents and exhibited
incomplete capacity in vivo for brief time frame periods.
Conclusion
The
dream of delivering truly regenerative or reconstituting cells, like endogenous
lung forebears or iPSCs, to the lung will require extra examination in creature
models before human application can be endeavored. On account of ESCs or iPSCs,
their intense separation and multiplication potential makes them dangerous and
conceivably teratogenic in human preliminaries, if they somehow happened to be
conveyed before their science is all the more completely comprehended.
Genuinely necessary examinations characterizing the hereditary and epigenetic
projects of these and other stem populaces are currently under way and should
assist with bettering characterize these phone populaces and their regenerative
potential.

Comments
Post a Comment